Quick Quiz: Can You Distinguish Sativa, Indica, and Hash?
Introduction
The world of cannabis is vast and intriguing. Whether it’s industrial hemp, recreational cannabis, or legal CBD, there are a multitude of varieties and products like Sativa flower, Indica flower, or the famous Hash. In Switzerland, the legislation on CBD products is quite specific, as the THC content must be below 1 percent to comply with legal standards (according to Article 2, Paragraph 1 of the Federal Act on Narcotics and Psychotropic Substances, RS 812.121). The different variations of legal cannabis raise many questions and curiosity, especially when talking about Sativa, Indica, or Hash.
In this long article, we offer you a quick quiz to assess your knowledge of these three major categories, while providing reliable and sourced information. We will also delve into the criteria for distinguishing between Sativa and Indica (related to their morphology and cannabinoid profile), Hash production, consumption methods, and Swiss legislation. Relax, read carefully, and discover a fascinating universe through the questions and answers.
Quick Quiz: Are You an Expert on Sativa, Indica, and Hash?
We will start with a few questions to test your knowledge. The goal is not to be an expert right away, but rather to discover how these varieties differ and how CBD Hash is produced. So, take a few minutes to read these questions and note your answers mentally or on a piece of paper. Detailed answers will follow in the next sections of the article.
Questions
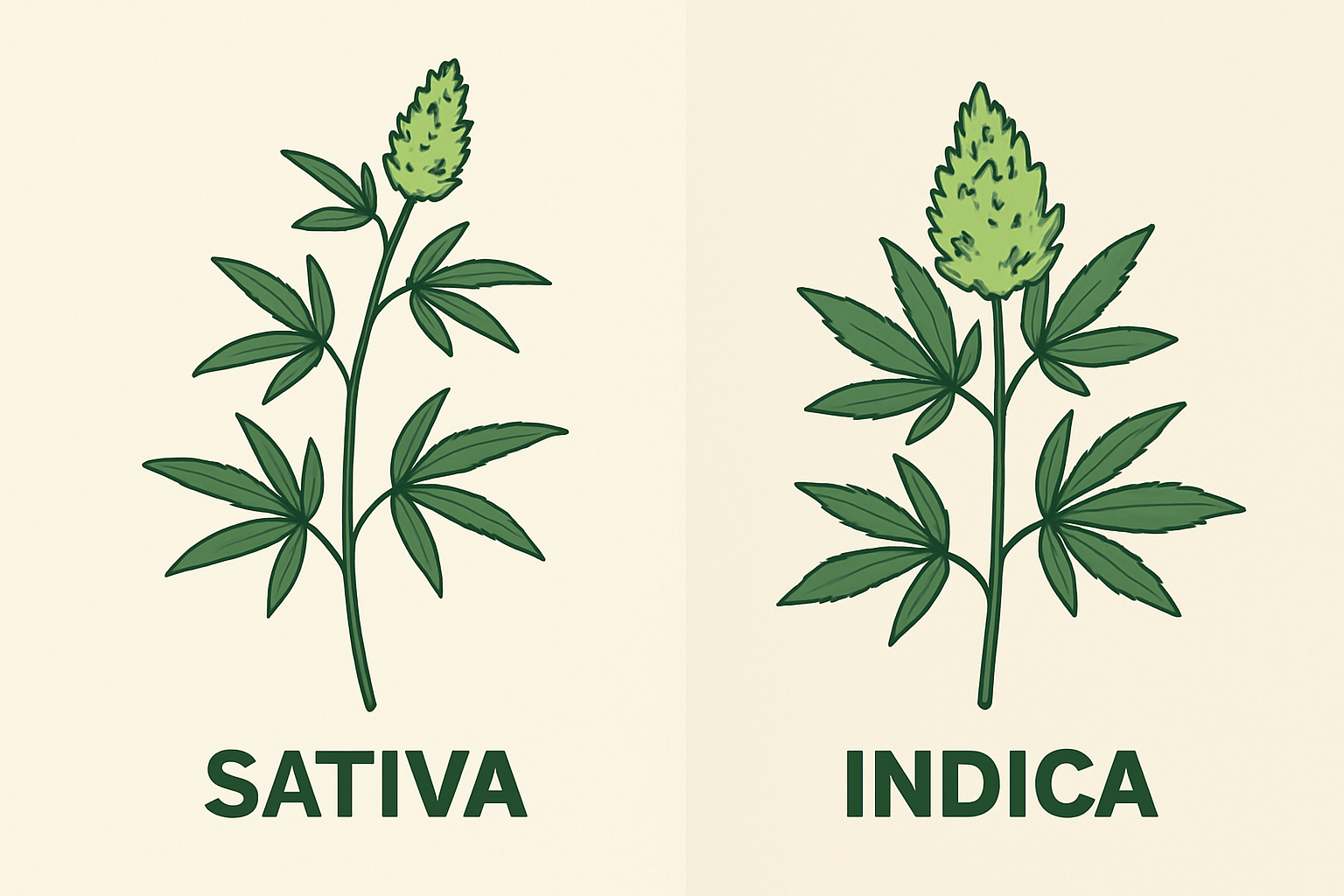
- What morphological characteristic is generally associated with a Sativa plant compared to an Indica plant?
- What is the maximum THC level a CBD variety must adhere to in order to be considered legal in Switzerland?
- What primarily differentiates the production of CBD Hash resin from simply drying cannabis flowers?
- In what type of climate is the Indica variety historically known to thrive?
- What historical use is associated with Hash in certain regions of the world (e.g., the Middle East)?
- What is the Swiss regulatory body responsible for overseeing and regulating cannabis legislation in Switzerland?
- What chemical parameter is often measured by liquid or gas chromatography in analysis laboratories to differentiate Sativa, Indica, and Hash?
- If it’s too hot and humid, what is the most common consequence on the preservation of CBD Hash?
- What is the benefit of combining different terpenes in the production of CBD Hash?
- What is the main reason for drying cannabis flowers (Sativa or Indica) before transforming them into Hash?
The answers are coming very soon. Before that, let’s explore in more detail the world of Sativa, Indica, and Hash, as well as the legal and scientific framework in Switzerland.
Sativa: The “Tall” Lady of Cannabis
Morphology and Origin
Sativa is renowned for being a relatively tall plant, capable of reaching significant heights outdoors (up to 3 meters or more, depending on the environment). According to a review published in Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research (2019), this Sativa distinction is largely due to its genetic heritage and specific growing conditions, including warmer climates and longer days. Its leaves typically have thin and long lobes, a morphological characteristic frequently used to distinguish it from Indica.
Historically, Sativa is reputed to originate mainly from equatorial regions such as Central Africa, Southeast Asia, and certain areas of Latin America. In these territories, the plant has adapted to an environment where the sunlight rate remains high. The flowering cycle of a Sativa is longer than that of an Indica, precisely because of this adaptation to hot and humid climates.
Cannabinoid and Terpene Profile
Numerous studies, including research published in Frontiers in Plant Science (2018), suggest that Sativa sometimes develops a richer profile in certain so-called “energizing” terpenes (to be taken with caution, as the notion of an energizing effect is also subjective). Sativa cannabis varieties have often been associated with variable concentrations of CBD and THC. For legal CBD specialty in Switzerland, cultivars (cultivated varieties) are selected that have a THC level not exceeding 1 percent. This is measured through laboratory analyses (often liquid or gas chromatography).
Use in Switzerland
Sativa hemp, listed among the legal varieties benefiting from federal authorizations, is produced for various reasons:
- Sativa flower rich in CBD.
- Seeds that can be used for food (hemp oil).
- Fibers, used in ecological construction or textile manufacturing.
According to the Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH), these multiple applications are authorized as long as producers respect the legal THC limit set in Switzerland at 1 percent (https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/fr/home/gesetze-und-bewilligungen/gesetze-und-verordnungen-im-bereich-sucht/cannabis.html). The traceability of production and compliance with organic or high-quality ecological cultivation standards are also concerns.
Indica: A Sturdy and Robust Plant
Origin and Preferred Climate
Indica, often associated with colder and mountainous regions of Asia (such as the Hindu Kush, north of Afghanistan), is traditionally a shorter and more compact plant than Sativa. The stems are thicker, the leaves wider, and the plant’s habit is more bushy. According to a review of botanical literature by the International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2020), Indica has developed morphological characteristics to adapt to harsh climatic conditions, such as significant temperature fluctuations and shorter growing seasons.
Specific Cannabinoid Profile
Referring to the same review Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research (2019), it is noted that some modern Indica phenotypes present a different THC/CBD ratio than those of Sativas. However, for legal CBD cultivation in Switzerland, Indica genetics are frequently crossed with strains rich in cannabidiol to keep THC below the 1 percent threshold. Laboratories perform tests by mass spectrometry or chromatography to verify legal compliance. Terpenes present in Indica may include myrcene, caryophyllene, or linalool, each possessing a distinct olfactory profile.
Uses and Legality
In Switzerland, if the plant is grown for CBD, it must comply with the same standards as Sativa (notably the maximum THC limit). Indica varieties hybridized for the legal market are thus found in various products:
- CBD flowers (sometimes used in infusion or vaporization).
- Concentrated oils.
- Concentrates such as Hash or “Charas” (a form of resin obtained by rubbing).
Everything must systematically be accompanied by a laboratory report proving that the THC level remains below 1 percent. Swiss growers often submit periodic samples for analysis to secure the commercialization of their products.
Hash: An Ancestral Art and a Sought-After Resin
Historical Origin
Hash (or hashish) is a resin extracted from cannabis trichomes. Historically, the use of Hash dates back several centuries, notably in the Middle East, Central Asia, and India. Medical texts and accounts of Arab travelers testify to resinous preparations used for both medicinal and recreational purposes. According to an article in the British Journal of Pharmacology (2018), these resins contain higher concentrations of cannabinoids, with trichomes being the richest part in active substances.
Modern Production Methods
To obtain CBD Hash, one usually starts with legal hemp varieties (Sativa or Indica) whose THC level does not exceed the Swiss legal limit. The production steps include:
- Harvesting the plants, followed by a drying and curing period.
- Separating the trichomes (dry or using dry ice or ice water, in the case of “bubble hash”).
- Sieving or beating the flowers to collect the resin powder (kief).
- Compressing the resin to form Hash blocks.
Some artisanal methods involve manually rubbing fresh flowers (similar to Charas in India). However, to ensure that the Hash remains below 1 percent THC and has an adequate CBD content, the plant must obviously be selected and the resin tested in a laboratory. According to the criteria established by the FOPH, the commercialization of CBD Hash is subject to the same rules as flowers: traceability, analyses, and precise labeling.
Conservation
Hash, due to its texture and high concentration of terpenes and cannabinoids, requires proper storage to prevent the active ingredients from degrading too quickly. Ideally, it is stored in an airtight container, away from light and in a dry place. Excessive humidity can lead to mold growth, while prolonged exposure to heat degrades cannabinoids. Keeping a storage journal, regularly checking the appearance and texture of Hash, and having it analyzed in case of doubt are good practices to preserve its quality over the long term.
Quiz Answers
Now that we have explored the basics of Sativa, Indica, and Hash, it’s time to unveil the answers to the ten questions posed above.
-
Morphological characteristic associated with Sativa
Sativa is generally taller and slender, with leaves having thin and long lobes. -
Maximum legal THC level in Switzerland
THC must be below 1 percent (Art. 2, Federal Act on Narcotics, RS 812.121). -
Main difference in Hash production compared to drying
To make Hash, trichomes (resin) are isolated and concentrated, unlike simply drying the flowers, which would be ready to consume or process directly. -
Climate favorable to Indica
Indica historically adapts to colder and mountainous climates (e.g., Hindu Kush regions). -
Historical use of Hash
In some regions (Middle East, Central Asia), Hash has been used for centuries for medicinal and recreational purposes. -
Swiss regulatory body
The Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is the main body that oversees and supervises cannabis legislation in Switzerland. -
Chemical parameter measured by chromatography
The THC and CBD levels (and sometimes other cannabinoids like CBG), as well as the presence of terpenes. -
Consequence of too hot and humid climate on Hash preservation
Risk of mold growth and faster degradation of cannabinoids. -
Interest in combining different terpenes
Combining various terpenes allows for a more complex aromatic spectrum and, according to some studies, may potentially influence the entourage effect (see an article in Frontiers in Neurology, 2018). -
Reason for drying flowers
Drying removes excess moisture, facilitating handling, preventing mold, and preparing the plant material for trichome extraction.
Swiss Legislation: Key Points to Remember
1 Percent THC Threshold
In Switzerland, the law is very clear: whether it’s flowers (Sativa or Indica) or resin (Hash), the THC level must remain below 1 percent. Beyond that, the product is considered an illegal narcotic, subject to the penal provisions of the Narcotics Act. This Swiss peculiarity (compared to other European countries that set the limit at 0.2 or 0.3 percent) offers a more flexible market for CBD while maintaining a strict regulatory framework, led by the FOPH.
Quality Control
CBD producers and distributors are subject to controls. Generally, this includes:
- Precise analysis certificates indicating the percentage of THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids.
- Assurance that the cultivation does not contain harmful substances like illegal pesticides, heavy metals, or residual solvents.
- Informative labeling, compliant with current legal standards.
Official controls help protect the consumer and preserve the reputation of a Swiss sector focused on quality.
Export and Import
In the case of CBD Hash, some countries with a lower THC limit may block the product’s entry into their territory, even if your Hash contains less than 1 percent THC. It is therefore important to check the legislation of the destination country before any export. Conversely, the import of Hash or other CBD products into Switzerland is possible if they comply with Swiss standards, notably the maximum THC level.
Consumption Methods and Practical Advice
Mode of Use for CBD Hash
CBD Hash can be consumed in various ways:
- By vaporization, using suitable devices (at medium temperature, to extract cannabinoids without combustion).
- In infusion, although the resin does not dissolve in water. It is then recommended to add a fat (e.g., whole milk).
- In certain culinary preparations (pastries, sauces), but always ensuring precise dosage.
However, it is important to remember that combustion (joint) is not recommended for health reasons. Scientific studies, including one published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (2015), indicate that smoke from combustion, regardless of the product, can be harmful to the respiratory system.
Conservation of Sativa or Indica Flowers
If you prefer to consume Sativa or Indica flowers directly in the form of tea, vaporization, or in cooking, it is essential to store them in airtight containers, away from light. Hemp flowers also degrade over time, especially if exposed to oxygen and humidity. Proper storage helps preserve terpenes, these aromatic molecules so important for the taste and smell of cannabis.
Avoiding Self-Medication
Although CBD is not psychoactive like THC, it can interact with certain medications (e.g., those metabolized by the liver via the cytochrome P450). For anyone wishing to use CBD for therapeutic purposes (anxiety, chronic pain, etc.), it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional to assess the dosage and relevance of such use. The available legal and scientific information (such as those listed by the FOPH or in medical journals) are good reference sources, but nothing replaces personalized advice from a doctor.
Some Tips for Better Success in Cannabis Quizzes
To deepen your knowledge:
-
Research in Scientific Journals
Publications like Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, Frontiers in Plant Science, or other specialized journals regularly address discoveries concerning hemp cultivation, extraction, or pharmacology. -
Consult Official Websites
In Switzerland, the FOPH website (https://www.bag.admin.ch) and the federal register (Fedlex) remain the best sources to stay informed about the evolution of laws and ordinances. Indeed, the regulation on legal cannabis is constantly evolving and may vary depending on the cantons. -
Consult Professionals
Analysis laboratories, certified growers, or CBD advocacy associations in Switzerland (e.g., the Hemp Association, formerly “Hemp-info”) are relevant interlocutors to answer specific questions about dosage or legal compliance. -
Regularly Test Your Knowledge
Taking quizzes, participating in hemp awareness workshops, or following specific training can help stay up to date on legal and scientific information.
Conclusion
Distinguishing Sativa, Indica, and Hash requires both cultural, scientific, and legal knowledge. While Sativa appears as a tall form and loves tropical climates, Indica presents itself as a more robust plant from mountainous regions, and Hash, for its part, is obtained by harvesting and compressing trichomes.
In Switzerland, the legal peculiarity imposes a THC level below 1 percent, which directly shapes the production and commercialization of any form of CBD hemp. This rule guarantees an accessible and legal product while imposing rigorous quality controls. Information on morphology, production methods, conservation, and possible uses (whether in infusion, vaporization, or culinary use) is also essential for anyone wishing to learn more or consume responsibly.
By reviewing the ten questions of our quick quiz, you now have a small knowledge base to better identify the fundamental differences between Sativa and Indica and understand how Hash fits into this landscape. Do not hesitate to deepen your research by consulting other reliable sources, such as peer-reviewed scientific studies, Swiss legislative texts, and recognized laboratory reports. This will help you further refine your knowledge and exercise discernment to consume or recommend a CBD product with confidence.
The world of legal cannabis is expanding, and it is better to be interested in it by relying on serious and up-to-date resources. Whether you are a producer, curious, occasional consumer, or simply a botany enthusiast, knowing how to recognize and differentiate Sativa, Indica, and Hash is an essential first step to navigating this exciting field.